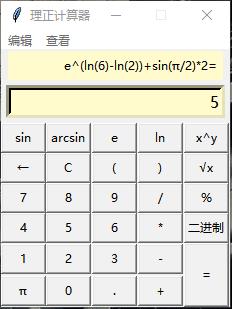
本文实例为大家分享了Python语言实现科学计算器的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下
自学Python语言一个月,还是小白,发一个科学计算器的代码,希望大家批评指正,共勉嘛。
calculator.py
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
|
from tkinter import *from functools import partialfrom calculate import *# 生成计算器主界面def buju(root): menu = Menu(root) # 菜单 submenu1 = Menu(menu, tearoff=0) # 分窗,0为在原窗,1为点击分为两个窗口 menu.add_cascade(label='编辑', menu=submenu1) # 添加子选项(label参数为显示内容) submenu1.add_command(label='复制', command=lambda: bianji(entry, 'copy')) # 添加命令 submenu1.add_command(label='剪切', command=lambda: bianji(entry, 'cut')) submenu1.add_command(label='粘贴', command=lambda: bianji(entry, 'paste')) submenu2 = Menu(menu, tearoff=0) menu.add_cascade(label='查看', menu=submenu2) submenu2.add_command(label='帮助', command=lambda: chakan(entry, 'help')) submenu2.add_command(label='作者', command=lambda: chakan(entry, 'author')) root.config(menu=menu) # 重新配置,添加菜单 label = Label(root, width=29, height=1, bd=5, bg='#FFFACD', anchor='se', textvariable=label_text) # 标签,可以显示文字或图片 label.grid(row=0, columnspan=5) # 布局器,向窗口注册并显示控件; rowspan:设置单元格纵向跨越的列数 entry = Entry(root, width=23, bd=5, bg='#FFFACD', justify="right", font=('微软雅黑', 12)) # 文本框(单行) entry.grid(row=1, column=0, columnspan=5, sticky=N + W + S + E, padx=5, pady=5) # 设置控件周围x、y方向空白区域保留大小 myButton = partial(Button, root, width=5, cursor='hand2', activebackground='#90EE90') # 偏函数:带有固定参数的函数 button_sin = myButton(text='sin', command=lambda: get_input(entry, 'sin(')) # 按钮 button_arcsin = myButton(text='arcsin', command=lambda: get_input(entry, 'arcsin(')) button_exp = myButton(text='e', command=lambda: get_input(entry, 'e')) button_ln = myButton(text='ln', command=lambda: get_input(entry, 'ln(')) button_xy = myButton(text='x^y', command=lambda: get_input(entry, '^')) button_sin.grid(row=2, column=0) button_arcsin.grid(row=2, column=1) button_exp.grid(row=2, column=2) button_ln.grid(row=2, column=3) button_xy.grid(row=2, column=4) button_shanyige = myButton(text='←', command=lambda: backspace(entry)) # command指定按钮消息的回调函数 button_shanquanbu = myButton(text=' C ', command=lambda: clear(entry)) button_zuokuohao = myButton(text='(', command=lambda: get_input(entry, '(')) button_youkuohao = myButton(text=')', command=lambda: get_input(entry, ')')) button_genhao = myButton(text='√x', command=lambda: get_input(entry, '√(')) button_shanyige.grid(row=3, column=0) button_shanquanbu.grid(row=3, column=1) button_zuokuohao.grid(row=3, column=2) button_youkuohao.grid(row=3, column=3) button_genhao.grid(row=3, column=4) button_7 = myButton(text=' 7 ', command=lambda: get_input(entry, '7')) button_8 = myButton(text=' 8 ', command=lambda: get_input(entry, '8')) button_9 = myButton(text=' 9 ', command=lambda: get_input(entry, '9')) button_chu = myButton(text=' / ', command=lambda: get_input(entry, '/')) button_yu = myButton(text='%', command=lambda: get_input(entry, '%')) button_7.grid(row=4, column=0) button_8.grid(row=4, column=1) button_9.grid(row=4, column=2) button_chu.grid(row=4, column=3) button_yu.grid(row=4, column=4) button_4 = myButton(text=' 4 ', command=lambda: get_input(entry, '4')) button_5 = myButton(text=' 5 ', command=lambda: get_input(entry, '5')) button_6 = myButton(text=' 6 ', command=lambda: get_input(entry, '6')) button_cheng = myButton(text=' * ', command=lambda: get_input(entry, '*')) button_jiecheng = myButton(text='二进制', command=lambda: jinzhi(entry)) button_4.grid(row=5, column=0) button_5.grid(row=5, column=1) button_6.grid(row=5, column=2) button_cheng.grid(row=5, column=3) button_jiecheng.grid(row=5, column=4) button_1 = myButton(text=' 1 ', command=lambda: get_input(entry, '1')) button_2 = myButton(text=' 2 ', command=lambda: get_input(entry, '2')) button_3 = myButton(text=' 3 ', command=lambda: get_input(entry, '3')) button_jian = myButton(text=' - ', command=lambda: get_input(entry, '-')) button_dengyu = myButton(text=' \n = \n ', command=lambda: calculator(entry)) button_1.grid(row=6, column=0) button_2.grid(row=6, column=1) button_3.grid(row=6, column=2) button_jian.grid(row=6, column=3) button_dengyu.grid(row=6, column=4, rowspan=2) # rowspan:设置单元格横向跨越的行数 button_pai = myButton(text=' π ', command=lambda: get_input(entry, 'π')) button_0 = myButton(text=' 0 ', command=lambda: get_input(entry, '0')) button_xiaoshudian = myButton(text=' . ', command=lambda: get_input(entry, '.')) button_jia = myButton(text=' + ', command=lambda: get_input(entry, '+')) button_pai.grid(row=7, column=0) button_0.grid(row=7, column=1) button_xiaoshudian.grid(row=7, column=2) button_jia.grid(row=7, column=3)# 对文本框中的算式或答案进行复制、剪切或粘贴def bianji(entry, argu): """ :param entry: 文本框 :param argu: 按钮对应的值 """ if argu == 'copy': entry.event_generate("<<Copy>>") elif argu == 'cut': entry.event_generate("<<Cut>>") clear(entry) elif argu == 'paste': entry.event_generate("<<Paste>>")# 查看使用帮助和作者信息def chakan(entry, argu): root = Tk() root.resizable(0, 0) text = Text(root, width=20, height=2, bd=5, bg='#FFFACD', font=('微软雅黑', 12)) text.grid(padx=5, pady=5) if argu == 'help': root.title('帮助') text.insert(INSERT, '这个计算器多简单!\n') text.insert(INSERT, '就别跟我要帮助了!') elif argu == 'author': root.title('作者') text.insert(INSERT, 'Author:冀梁栋\n') text.insert(INSERT, 'Time:2019-07-08')# 删除最后一次输入内容def backspace(entry): entry.delete(len(entry.get()) - 1) # 删除文本框的最后一个输入值# 删除所有输入内容和显示内容def clear(entry): entry.delete(0, END) # 删除文本框的所有内容 label_text.set('')# 点击计算器输入按钮后向文本框中添加内容def get_input(entry, argu): formula = entry.get() for char in formula: if '\u4e00' <= char <= '\u9fa5': clear(entry) # 删除文本框中的汉字显示,减少手动删除操作 entry.insert(INSERT, argu) # 使用END时,键盘敲入和按键输入组合操作会出错# 十进制整数转换为二进制整数def jinzhi(entry): try: formula = entry.get() if re.match('\d+$', formula): number = int(formula) cunchu = [] # 放置每次除以2后的余数 result = '' while number: cunchu.append(number % 2) number //= 2 # 整数除法,返回商 while cunchu: result += str(cunchu.pop()) # 将所有余数倒置得到结果 clear(entry) entry.insert(END, result) label_text.set(''.join(formula + '=')) else: clear(entry) entry.insert(END, '请输入十进制整数') except: clear(entry) entry.insert(END, '出错')# 点击“=”后进行计算def calculator(entry): try: formula = entry.get() # 输入内容只是数字或π或e时,仍显示该内容 if re.match('-?[\d+,π,e]\.?\d*$', formula): label_text.set(''.join(formula + '=')) return # 输入内容是算式时,显示其计算结果 result = final_calc(formula_format(formula)) clear(entry) entry.insert(END, result) # 将结果输出到文本框中 label_text.set(''.join(formula + '=')) except: clear(entry) entry.insert(END, '出错')if __name__ == '__main__': root = Tk() # 生成窗口 root.title('理正计算器') # 窗口的名字 root.resizable(0, 0) # 窗口大小可调性,分别表示x,y方向的可变性 global label_text # 定义全局变量 label_text = StringVar() buju(root) root.mainloop() # 进入消息循环(必需组件),否则生成的窗口一闪而过 |
calculate.py
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
|
import refrom math import *# 将算式从字符串处理成列表,解决横杠是负号还是减号的问题def formula_format(formula): """ :param formula: str """ formula = re.sub(' ', '', formula) # 去掉算式中的空格s # 以 '横杠数字' 分割, 其中正则表达式:(\-\d+\.?\d*) 括号内: # \- 表示匹配横杠开头;\d+ 表示匹配数字1次或多次;\.?表示匹配小数点0次或1次;\d*表示匹配数字0次或多次。 formula_list = [i for i in re.split('(-[\d+,π,e]\.?\d*)', formula) if i] final_formula = [] # 最终的算式列表 for item in formula_list: # 算式以横杠开头,则第一个数字为负数,横杠为负号 if len(final_formula) == 0 and re.match('-[\d+,π,e]\.?\d*$', item): final_formula.append(item) continue # 如果当前的算式列表最后一个元素是运算符['+', '-', '*', '/', '(', '%', '^'], 则横杠为减号 if len(final_formula) > 0: if re.match('[\+\-\*\/\(\%\^]$', final_formula[-1]): final_formula.append(item) continue # 按照运算符分割开 item_split = [i for i in re.split('([\+\-\*\/\(\)\%\^\√])', item) if i] final_formula += item_split return final_formula# 判断是否是运算符,如果是返回Truedef is_operator(e): """ :param e: str :return: bool """ opers = ['+', '-', '*', '/', '(', ')', '%', '^', '√', 'sin', 'arcsin', 'ln'] return True if e in opers else False # 在for循环中嵌套使用if和else语句# 比较连续两个运算符来判断是压栈还是弹栈def decision(tail_op, now_op): """ :param tail_op: 运算符栈的最后一个运算符 :param now_op: 从算式列表取出的当前运算符 :return: 1代表弹栈运算,0代表弹出运算符栈最后一个元素'(',-1表示压栈 """ # 定义4种运算符级别 rate1 = ['+', '-'] rate2 = ['*', '/', '%'] rate3 = ['^', '√', 'sin', 'arcsin', 'ln'] rate4 = ['('] rate5 = [')'] if tail_op in rate1: if now_op in rate2 or now_op in rate3 or now_op in rate4: return -1 # 说明当前运算符优先级高于运算符栈的最后一个运算符,需要压栈 else: return 1 # 说明当前运算符优先级等于运算符栈的最后一个运算符,需要弹栈运算 elif tail_op in rate2: if now_op in rate3 or now_op in rate4: return -1 else: return 1 elif tail_op in rate3: if now_op in rate4: return -1 else: return 1 elif tail_op in rate4: if now_op in rate5: return 0 # '('遇上')',需要弹出'('并丢掉')',表明该括号内的算式已计算完成并将结果压入数字栈中 else: return -1 # 只要栈顶元素为'('且当前元素不是')',都应压入栈中# 传入两个数字,一个运算符,根据运算符不同返回相应结果def calculate(n1, n2, operator): """ :param n1: float :param n2: float :param operator: + - * / % ^ :return: float """ result = 0 if operator == '+': result = n1 + n2 if operator == '-': result = n1 - n2 if operator == '*': result = n1 * n2 if operator == '/': result = n1 / n2 if operator == '%': result = n1 % n2 if operator == '^': result = n1 ** n2 return result# 括号内的算式求出计算结果后,计算√()、sin()或arcsin()def gaojie(op_stack, num_stack): if op_stack[-1] == '√': op = op_stack.pop() num2 = num_stack.pop() num_stack.append(sqrt(num2)) elif op_stack[-1] == 'sin': op = op_stack.pop() num2 = num_stack.pop() num_stack.append(sin(num2)) elif op_stack[-1] == 'arcsin': op = op_stack.pop() num2 = num_stack.pop() num_stack.append(asin(num2)) elif op_stack[-1] == 'ln': op = op_stack.pop() num2 = num_stack.pop() num_stack.append(log(num2))# 负责遍历算式列表中的字符,决定压入数字栈中或压入运算符栈中或弹栈运算def final_calc(formula_list): """ :param formula_list: 算式列表 :return: 计算结果 """ num_stack = [] # 数字栈 op_stack = [] # 运算符栈 for item in formula_list: operator = is_operator(item) # 压入数字栈 if not operator: # π和e转换成可用于计算的值 if item == 'π': num_stack.append(pi) elif item == '-π': num_stack.append(-pi) elif item == 'e': num_stack.append(e) elif item == '-e': num_stack.append(-e) else: num_stack.append(float(item)) # 字符串转换为浮点数 # 如果是运算符 else: while True: # 如果运算符栈为空,则无条件入栈 if len(op_stack) == 0: op_stack.append(item) break # 决定压栈或弹栈 tag = decision(op_stack[-1], item) # 如果是-1,则压入运算符栈并进入下一次循环 if tag == -1: op_stack.append(item) break # 如果是0,则弹出运算符栈内最后一个'('并丢掉当前')',进入下一次循环 elif tag == 0: op_stack.pop() gaojie(op_stack, num_stack) # '('前是'√'、'sin'或'arcsin'时,对括号内算式的计算结果作相应的运算 break # 如果是1,则弹出运算符栈内最后一个元素和数字栈内最后两个元素 elif tag == 1: if item in ['√', 'sin', 'arcsin']: op_stack.append(item) break op = op_stack.pop() num2 = num_stack.pop() num1 = num_stack.pop() # 将计算结果压入数字栈并接着循环,直到遇到break跳出循环 num_stack.append(calculate(num1, num2, op)) # 大循环结束后,数字栈和运算符栈中可能还有元素的情况 while len(op_stack) != 0: op = op_stack.pop() num2 = num_stack.pop() num1 = num_stack.pop() num_stack.append(calculate(num1, num2, op)) result = str(num_stack[0]) # 去掉无效的0和小数点,例:1.0转换为1 if result[len(result) - 1] == '0' and result[len(result) - 2] == '.': result = result[0:-2] return resultif __name__ == '__main__': # formula = "2 * ( 3 - 5 * ( - 6 + 3 * 2 / 2 ) )" formula = "arcsin ( 0 )" formula_list = formula_format(formula) result = final_calc(formula_list) print("算式:", formula) print("计算结果:", result) |
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_30475405/article/details/96870126